Why Istio
Microservices Sprawl
Cloud-native applications are architected as a constellation of distributed microservices, which run in containers, orchestrated through kubernetes. Adopting a microservices architecture brings a host of benefits, including increased autonomy, flexibility and modularity. But the process of decoupling a monolithic application into smaller services introduces new obstacles: How do you know what’s running? How do you roll out new versions of your services? How do you secure and monitor all those containers?
Most companies using microservices architecture don’t fully understand until they are well down the path about microservices sprawl. The number of small services that are deployed expand exponentially and this exponential growth in microservices creates challenges around figuring out how to enforce and standardize things like routing between multiple services/versions, authentication and authorization, encryption and load balancing within a Kubernetes cluster. Building on service mesh helps resolve some of these issues and more.
As containers abstract away the operating system from the application, a service mesh abstracts away how inter-process communications are handled. Istio is a widely adopted open-source service mesh that helps organizations run distributed, microservices-based apps. Its powerful features provide a uniform and more efficient way to secure, connect and monitor services, so DevOps can modernize their apps more swiftly and securely. Whether you’re building from scratch or migrating existing applications to cloud native, Istio addresses the challenges developers and operators face with a distributed or microservices architecture.
The Genesis of Istio
To explain what Istio is, it’s also important to understand the context in which Istio came into being — i.e., why is there an Istio?
Microservices are a technical solution to an organizational problem. And Kubernetes and Istio are technical solutions to deal with the issues created by moving to microservices. As a deliverable for microservices, containers solve the problem of environmental consistency and allow for more granularity in limiting application resources. They are widely used as a vehicle for microservices.
Google open-sourced Kubernetes in 2014, which grew exponentially over the next few years. It became a container scheduling tool to solve the deployment and scheduling problems of distributed applications — allowing you to treat many computers as though they were one computer. Because the resources of a single machine are limited and Internet applications may have traffic floods at different times (due to rapid expansion of user scale or different user attributes), the elasticity of computing resources needs to be high. A single machine obviously can’t meet the needs of a large-scale application; and conversely, it would be a huge waste for a very small-scale application to occupy the whole host. In short, Kubernetes defines the final state of the service and enables the system to reach and stay in that state automatically.
What is Istio?
Istio is an open-source service mesh that helps organizations run distributed, microservices-based apps. It provides a way to secure, connect and monitor microservices. Istio layers transparently onto existing distributed applications and sits as an overlay between the layers of distributed applications. Istio works natively with Kubernetes (K8s) only, but its open source nature makes it possible for anyone to write extensions enabling Istio to run on any cluster software. Istio includes APIs that let Istio integrate into any logging platform, telemetry or policy system. Istio enables intelligent application-aware load balancing from the application layer to other mesh-enabled services in the cluster. It bypasses the rudimentary kube-proxy load balancing.
Istio’s powerful control plane brings vital features including:
- Secure service-to-service communication in a cluster with TLS encryption, strong identity-based authentication and authorization
- Automatic load balancing for HTTP, gRPC, WebSocket and TCP traffic
- Fine-grained control of traffic behavior with rich routing rules, retries, failovers, and fault injection
- A pluggable policy layer and configuration API supporting access controls, rate limits and quotas
- Automatic metrics, logs and traces for all traffic within a cluster, including cluster ingress and egress
How it Works
Istio’s core consists of a control plane and a data plane, with Envoy as the default data-plane agent. The following diagram shows the various components of each plane:
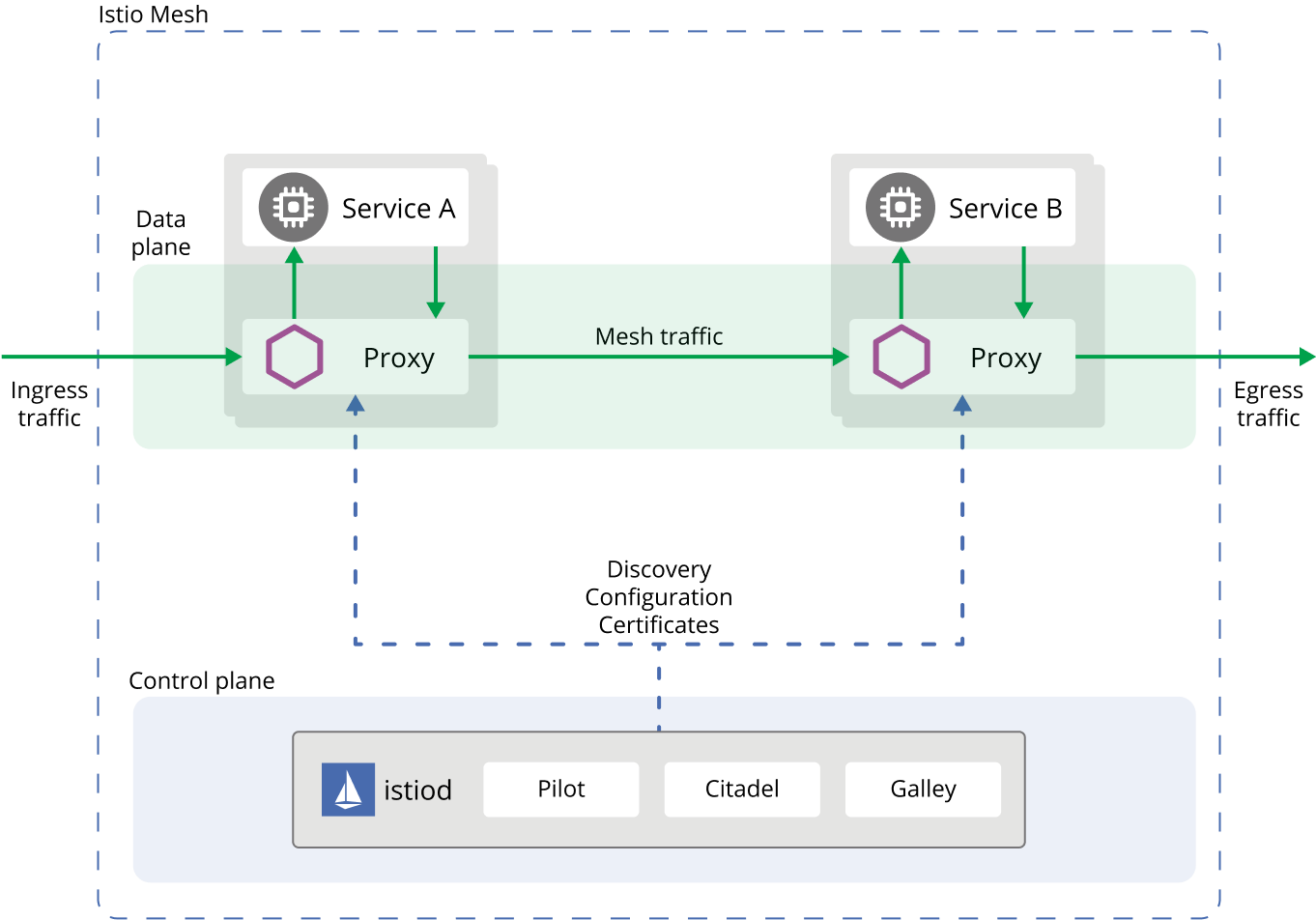
Istio is designed for extensibility and can handle a diverse range of deployment needs. Istio’s control plane runs on Kubernetes and you can add applications deployed in that cluster to your mesh, extend the mesh to other clusters, or even connect VMs or other endpoints running outside of Kubernetes.
How do Istio, Envoy and Kubernetes work together?
The key to understanding Isto and the Istio architecture is to understand both Envoy and Kubernetes. It’s not a question of Istio versus Envoy or Istio versus Kubernetes - they often work together to make a microservices-based containerized environment operate smoothly. For example, service meshes like Istio are made up of both a control plane and a data plane. Istio uses an extended version of Envoy as its data plane. Envoy then manages all inbound and outbound traffic in the Istio service mesh. Kubernetes is an open source platform that gets rid of many of the manual processes involved in deploying and scaling containerized applications by automating and orchestrating them. And although Istio is platform independent, using Istio and Kubernetes together is popular among developers. In addition, Kubernetes stands as a cornerstone for building cloud-native applications. It offers key features such as self-healing capabilities, service discovery, load balancing and secret management, which are essential for running applications at scale in distributed environments. Its inherent support for mulit-cloud deployments, microservices architecture and CI/CD pipelines positions it as a pivotal element in the DevOps and cloud computing ecosystems.
Get Started
Tetrate offers training and certification to turbo-charge your service mesh journey.